An autonomous AI agent is a self-governing system designed to perceive its environment, process information, and take actions to achieve specific objectives with minimal human oversight. Unlike basic automation tools that follow pre-programmed instructions, these agents continuously learn, adapt, and improve their decision-making abilities.
Table of Contents
Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents have rapidly evolved from simple rule-based programs to sophisticated autonomous systems capable of making complex decisions in real time. These AI-powered entities are designed to perceive their environment, process information, and take actions to achieve specific goals—often without human intervention.
From chatbots handling customer service inquiries to self-driving cars navigating busy streets, AI agents are transforming the way we interact with technology. They seamlessly integrate into various industries, automating tasks that once required human intelligence, reducing operational costs, and improving efficiency. But beyond just automation, these agents are now capable of learning, adapting, and improving their performance over time, making them an indispensable part of the digital age.
As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on AI-driven automation, one question stands out: How are autonomous AI agents reshaping the world around us, and what does this mean for the future of work, productivity, and innovation?
Why Autonomous AI Agents Are Revolutionizing Industries
AI is no longer confined to research labs and tech giants. Today, autonomous AI agents are making a profound impact across multiple industries, revolutionizing the way tasks are executed and decisions are made. But what makes these AI-driven systems so transformative?
1. Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity
Traditional automation required rigid programming and predefined rules, but AI agents take it to the next level by dynamically adjusting to new situations. In industries like manufacturing, AI-powered robots can self-optimize their processes, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency. In finance, intelligent algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data in seconds, detecting fraudulent activities and making real-time trading decisions.
2. Reducing Human Workload and Errors
Human errors can be costly, especially in fields like healthcare and cybersecurity. AI agents are stepping in to handle repetitive, high-stakes tasks with precision. For instance, AI-powered diagnostic systems can analyze medical scans more accurately than human doctors, catching diseases at early stages. In cybersecurity, autonomous AI systems detect and neutralize threats faster than traditional security measures.
3. Personalization at Scale
The rise of AI agents has ushered in a new era of hyper-personalization. Whether it’s streaming services recommending content, virtual assistants tailoring responses, or e-commerce platforms curating product suggestions, AI-driven personalization is redefining customer experiences. These agents continuously learn from user behavior, ensuring that interactions become more relevant and engaging over time.
4. Accelerating Scientific and Technological Advancements
AI agents are not just automating existing processes; they’re also pushing the boundaries of innovation. In pharmaceuticals, AI-driven research tools are speeding up drug discovery by analyzing molecular structures in ways humans never could. In space exploration, autonomous AI is enabling rovers and satellites to navigate unknown terrains and gather crucial data without human intervention.
5. Transforming Decision-Making and Strategy
Data-driven decision-making is crucial in today’s fast-paced business landscape, and AI agents are making this process smarter than ever. From optimizing supply chains to predicting market trends, these agents provide actionable insights that help organizations stay ahead of the competition. Their ability to process and analyze vast datasets in real-time allows leaders to make informed decisions with unprecedented accuracy.
What Are Autonomous AI Agents?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved beyond simple automation, giving rise to autonomous AI agents—intelligent systems capable of operating independently, making decisions, and adapting to dynamic environments without constant human intervention. These AI-driven entities are revolutionizing industries by taking on complex tasks that require reasoning, learning, and problem-solving, making them far more advanced than traditional AI models.
But what exactly makes an AI agent “autonomous,” and why is this capability so transformative?
Definition and Key Characteristics
An autonomous AI agent is a self-governing system designed to perceive its environment, process information, and take actions to achieve specific objectives with minimal human oversight. Unlike basic automation tools that follow pre-programmed instructions, these agents continuously learn, adapt, and improve their decision-making abilities.
Key characteristics of autonomous AI agents include:
- Perception & Awareness – They collect and interpret data from their surroundings using sensors, cameras, or digital inputs.
- Decision-Making Capabilities – They analyze information, weigh options, and choose the best course of action based on predefined goals.
- Adaptability & Learning – Many use machine learning (ML) and deep learning to evolve over time, improving performance through experience.
- Autonomy – They function with minimal or no human intervention, making independent decisions to optimize efficiency.
- Goal-Oriented Behavior – They work toward specific objectives, whether it’s optimizing a supply chain, detecting cybersecurity threats, or assisting in medical diagnoses.
These characteristics allow AI agents to operate in unpredictable environments, making them useful across diverse industries, from robotics and finance to healthcare and customer service.
How They Differ from Traditional AI Systems
While traditional AI systems have paved the way for automation, they operate under fixed rule-based frameworks that limit their ability to adapt to new scenarios. Here’s how autonomous AI agents stand apart:
| Feature | Traditional AI Systems | Autonomous AI Agents |
| Dependency on Humans | Requires frequent human input | Functions with minimal oversight |
| Adaptability | Pre-programmed; struggles with new situations | Learns and adapts dynamically |
| Decision-Making | Follows strict rules and logic | Evaluates situations and makes real-time decisions |
| Complexity of Tasks | Best suited for repetitive, predictable tasks | Handles complex, dynamic tasks |
| Examples | Chatbots, recommendation engines | Self-driving cars, intelligent robots |
For instance, a traditional AI-powered chatbot follows scripted responses, while an autonomous AI agent in customer support can analyze past interactions, detect sentiment, and generate personalized solutions on the fly. Similarly, an AI-powered thermostat might adjust based on predefined temperature settings, while an autonomous AI-driven climate control system can predict temperature changes and self-optimize for energy efficiency.
The Importance of Autonomy and Adaptability
The rise of autonomous AI agents is not just a technological upgrade—it’s a fundamental shift in how we interact with machines and how industries operate. Their autonomy and adaptability provide several advantages:
- Increased Efficiency – AI agents reduce human workload, handle repetitive tasks, and optimize processes in real time.
- Better Decision-Making – They process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make informed choices faster than humans.
- Cost Reduction – By automating complex workflows, businesses save time and resources, leading to greater profitability.
- Scalability – Autonomous AI can handle expanding workloads without requiring additional human intervention.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving – Unlike rigid AI systems, autonomous agents can adapt to unforeseen challenges and create innovative solutions.
Take self-driving cars as an example. A traditional AI system might recognize traffic signs based on fixed patterns, but an autonomous vehicle can adjust its driving behavior in real-time, predict pedestrian movements, and react to sudden obstacles—all without human input. Similarly, autonomous cybersecurity agents don’t just detect known threats; they continuously learn new hacking techniques and preemptively neutralize attacks.
As industries embrace autonomy, the next frontier of AI will be about intelligent systems that not only automate tasks but also think, adapt, and evolve—pushing us closer to a world where AI acts as a true partner in innovation and progress.
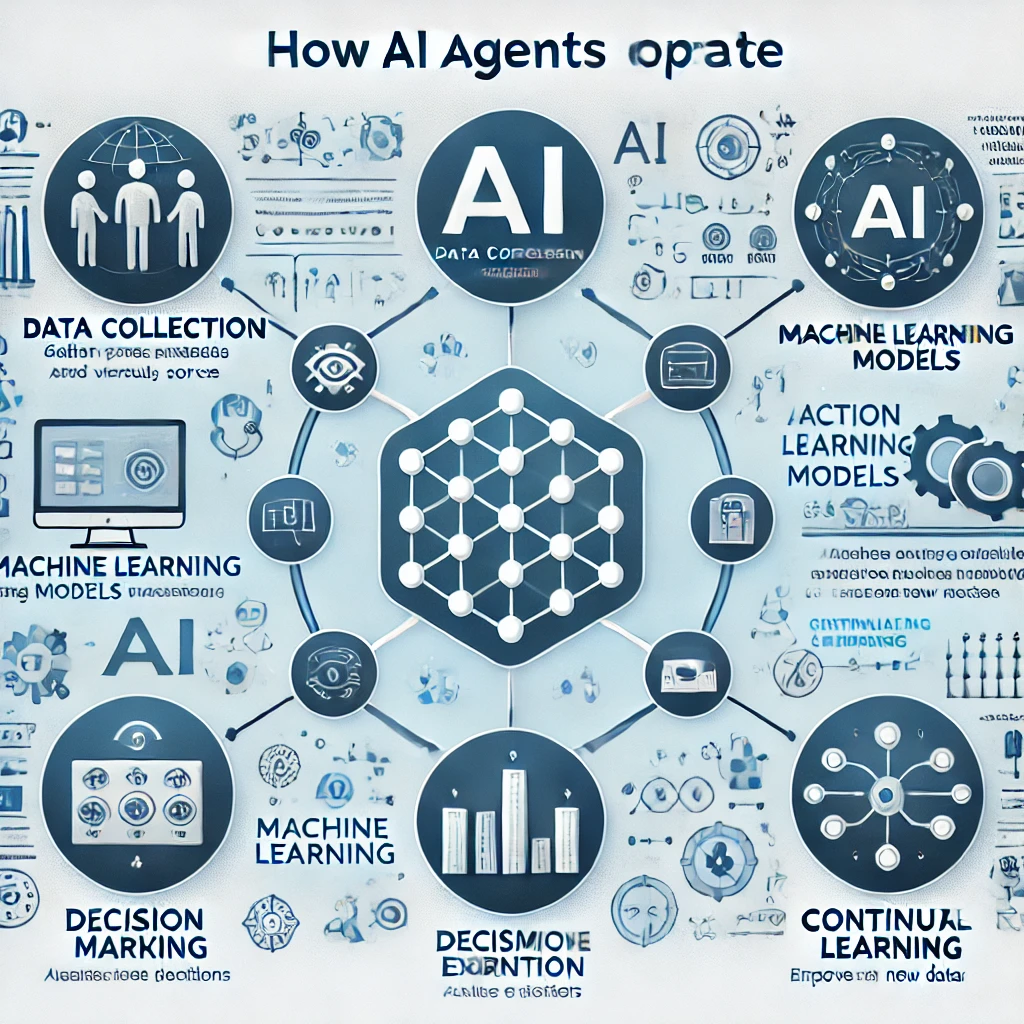
How AI Agents Operate
AI agents are more than just automated programs—they are intelligent systems capable of perceiving, learning, and making decisions in real time. Their ability to operate autonomously and adapt to changing environments is powered by a combination of advanced technologies that enable perception, reasoning, and action.
From self-driving cars navigating busy streets to AI-powered financial advisors predicting market trends, these intelligent agents rely on a sophisticated mix of machine learning, neural networks, natural language processing, and reinforcement learning to function effectively. But how do these technologies work together to enable AI agents to think and act independently?
The Underlying Technologies Powering Autonomous Agents
Autonomous AI agents are built on a foundation of cutting-edge AI technologies that allow them to process information, make decisions, and improve over time. Some of the core components that power these agents include:
- Machine Learning & Neural Networks – The ability to recognize patterns and improve through experience.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – The ability to understand and communicate using human language.
- Reinforcement Learning – A learning process based on trial and error to optimize decision-making.
- Decision-Making Algorithms – The logic that allows AI agents to choose the best course of action.
Each of these technologies plays a crucial role in making AI agents more intelligent, efficient, and autonomous. Let’s break them down further.
Machine Learning and Neural Networks: The Brain Behind AI Agents
At the heart of every AI agent lies machine learning (ML), a branch of AI that enables systems to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. These agents analyze vast amounts of information, recognize patterns, and refine their predictions over time.
How It Works:
- AI agents ingest data from their environment (e.g., images, text, or real-time inputs).
- Algorithms identify patterns and make predictions based on past experiences.
- The system continuously improves its accuracy as it processes more data.
Neural networks, inspired by the human brain, are a powerful subset of ML that help AI agents handle complex decision-making tasks. These networks consist of layers of artificial neurons that process information hierarchically, allowing AI to:
- Recognize images and objects (used in self-driving cars).
- Predict stock market trends (used in financial AI agents).
- Detect fraud (used in banking security systems).
For example, an AI-powered customer service bot using neural networks can analyze thousands of past interactions to predict what customers are asking—even if they phrase their questions differently.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): How AI Understands Human Language
One of the most impressive capabilities of AI agents is their ability to understand and communicate in natural language—a feat made possible by Natural Language Processing (NLP).
How NLP Powers AI Agents:
- Speech Recognition – Converts spoken language into text (e.g., virtual assistants like Siri).
- Sentiment Analysis – Understands emotions in text (e.g., analyzing customer reviews).
- Context Awareness – Recognizes context and intent rather than just keywords.
By leveraging NLP, AI agents can converse naturally with humans, making them invaluable in customer service, content generation, and even medical diagnosis. Virtual assistants like ChatGPT, Google Assistant, and Alexa are prime examples of AI agents using NLP to provide real-time responses and meaningful interactions.
Reinforcement Learning: Teaching AI Through Rewards and Penalties
Unlike traditional machine learning, which relies on labeled data, reinforcement learning (RL) allows AI agents to learn through trial and error by interacting with their environment.
How Reinforcement Learning Works:
- The AI takes an action in an environment.
- It receives positive or negative feedback (a “reward” or “penalty”).
- The AI adjusts its strategy to maximize rewards over time.
This method is especially useful in:
- Self-driving cars – Learning to navigate traffic by trial and error.
- Game-playing AI – Beating human champions in chess, Go, and video games.
- Robotics – Teaching robots to walk, grasp objects, or perform delicate surgeries.
For example, OpenAI’s AlphaGo defeated world champions in the game of Go by using reinforcement learning to develop strategies beyond human intuition.
The Decision-Making Process of AI Agents
AI agents follow a structured decision-making process, allowing them to analyze information and determine the best possible action. The process typically involves:
- Perception – Gathering data from sensors, cameras, or digital inputs.
- Analysis – Processing information using ML models and neural networks.
- Prediction – Forecasting possible outcomes based on patterns.
- Decision-Making – Choosing the optimal action using decision algorithms.
- Execution – Performing the selected action and learning from the results.
For example, in autonomous vehicles, this decision-making loop allows the car to:
- Detect pedestrians and obstacles.
- Predict the movement of other cars.
- Decide when to stop, accelerate, or change lanes.
Similarly, in AI-powered financial trading, agents continuously analyze stock market data to decide the best times to buy or sell shares, maximizing profits while minimizing risks.
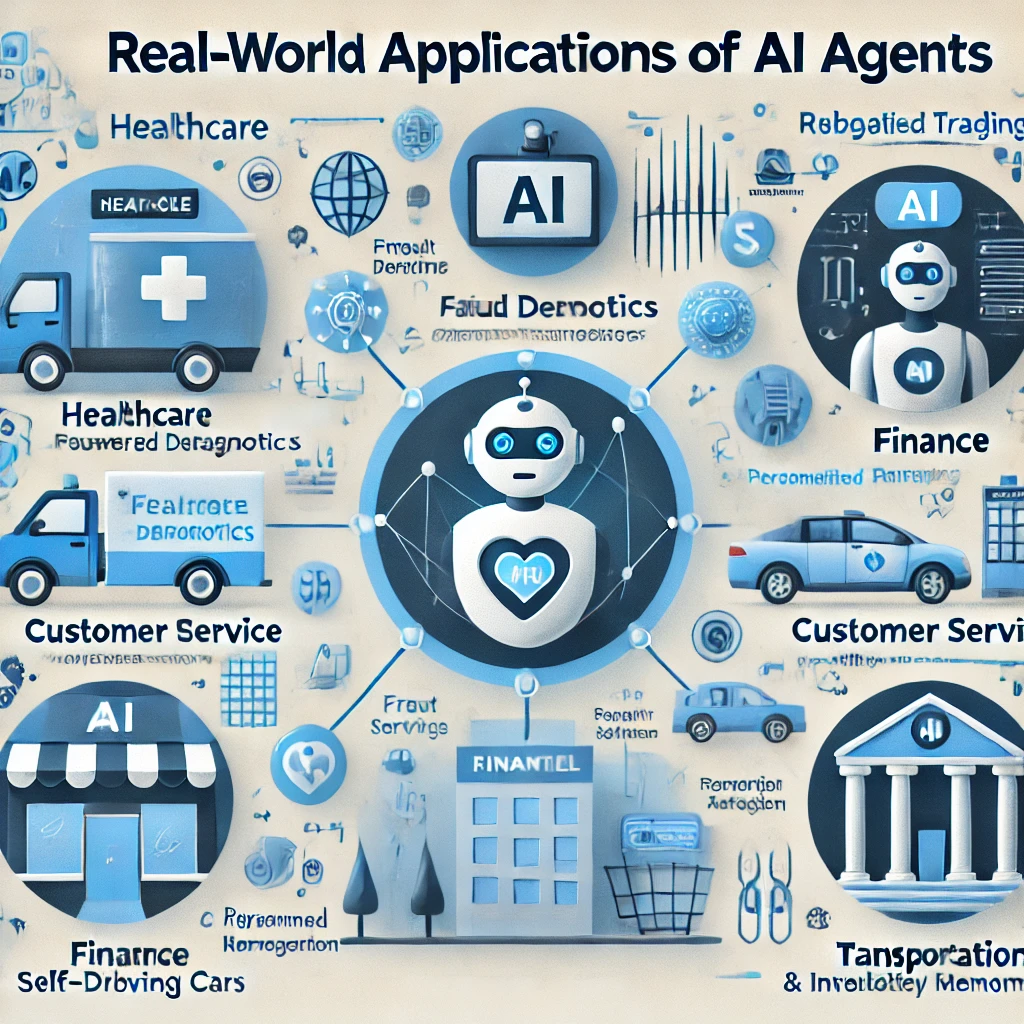
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are revolutionizing industries by automating tasks, optimizing workflows, and making intelligent decisions in real time. Unlike traditional software, these autonomous systems can learn, adapt, and operate independently, making them invaluable in a wide range of fields. From virtual assistants in customer service to AI-powered diagnostics in healthcare, these intelligent agents are enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving user experiences.
Let’s explore how AI agents are transforming different industries.
Customer Service Automation: AI-Powered Virtual Assistants & Chatbots
Customer service has been one of the most significant beneficiaries of AI-driven automation. Virtual assistants and chatbots powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP) are now handling millions of inquiries, providing faster and more efficient support than traditional call centers.
How AI Agents Enhance Customer Service:
- 24/7 Availability – AI chatbots provide instant responses without human intervention.
- Personalized Interactions – AI analyzes user history to tailor responses.
- Faster Query Resolution – AI can process and solve customer issues in seconds.
Real-World Examples:
✅ ChatGPT-based assistants – Companies use AI-driven chatbots to handle FAQs, troubleshooting, and customer inquiries.
✅ Voice assistants like Alexa & Siri – These AI agents understand commands, perform tasks, and provide recommendations.
✅ AI-powered email assistants – Systems like Gmail’s Smart Compose predict and suggest email responses.
The integration of AI in customer service is reducing wait times, increasing customer satisfaction, and saving companies millions in operational costs.
Healthcare Advancements: AI-Powered Diagnostics & Patient Management
AI agents are transforming healthcare by improving diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, and optimizing hospital operations. These AI-driven systems help doctors analyze medical data faster, detect diseases earlier, and improve patient outcomes.
How AI is Revolutionizing Healthcare:
- Early Disease Detection – AI scans medical images (MRIs, CT scans) to identify conditions like cancer.
- Automated Patient Monitoring – AI-powered systems track patient vitals in real time.
- Personalized Treatment Plans – AI recommends treatments based on patient history and genetic data.
Real-World Examples:
✅ IBM Watson Health – Uses AI to diagnose diseases and recommend treatments based on vast medical datasets.
✅ AI in Radiology – Google’s DeepMind AI detects eye diseases with higher accuracy than human doctors.
✅ AI-powered chatbots for mental health – Apps like Woebot provide cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) through conversational AI.
By automating diagnostics and enhancing doctor-patient interactions, AI agents are saving lives and making healthcare more accessible and efficient.
Supply Chain Optimization: AI Agents in Logistics & Inventory Management
The global supply chain is incredibly complex, requiring real-time monitoring, demand forecasting, and inventory management. AI agents are making supply chains more efficient, cost-effective, and resilient by optimizing logistics and predicting demand fluctuations.
How AI Improves Supply Chains:
- Demand Forecasting – AI predicts customer demand trends and prevents overstocking.
- Route Optimization – AI-powered GPS systems calculate the fastest and most cost-effective delivery routes.
- Automated Warehouses – AI-driven robots streamline inventory management and reduce human errors.
Real-World Examples:
✅ Amazon’s AI-powered warehouses – Robots and AI algorithms manage inventory and streamline order fulfillment.
✅ DHL’s predictive analytics – AI predicts supply chain disruptions and optimizes delivery routes.
✅ Walmart’s AI inventory tracking – AI-powered systems monitor stock levels and automate restocking.
By minimizing delays, cutting costs, and increasing efficiency, AI agents are reshaping the logistics industry.
Financial Services: AI in Trading & Fraud Detection
AI agents are revolutionizing banking, investing, and financial security by processing vast amounts of financial data in real time. These intelligent systems predict market trends, automate trading, and detect fraudulent transactions faster than humans ever could.
How AI is Changing Finance:
- AI Trading Bots – AI-driven algorithms execute stock trades at optimal times.
- Fraud Detection – AI monitors financial transactions for suspicious activity.
- Personalized Banking – AI-powered financial assistants provide budgeting advice and investment recommendations.
Real-World Examples:
✅ Goldman Sachs AI trading desks – AI agents execute stock trades faster than human traders.
✅ PayPal’s AI fraud detection – AI prevents millions of fraudulent transactions each year.
✅ Robo-advisors like Betterment & Wealthfront – AI provides personalized investment strategies with minimal fees.
By improving risk management, enhancing security, and optimizing trading strategies, AI agents are making financial markets more efficient and secure.
Manufacturing & Robotics: AI-Powered Smart Factories
Manufacturing is undergoing a major transformation with AI-driven smart factories that use robotics, predictive maintenance, and process automation. AI-powered agents reduce downtime, improve production quality, and optimize energy consumption.
How AI is Transforming Manufacturing:
- Predictive Maintenance – AI detects equipment failures before they happen, preventing costly downtime.
- Automated Assembly Lines – AI-powered robots increase production speed and accuracy.
- Quality Control – AI inspects products for defects using computer vision.
Real-World Examples:
✅ Tesla’s AI-driven factories – Robots powered by AI handle car assembly with extreme precision.
✅ Siemens’ Smart Factory – AI optimizes energy use and detects faults in real time.
✅ AI-powered quality control at BMW – AI inspects car components to ensure they meet quality standards.
AI-driven automation is boosting production efficiency, lowering costs, and making factories safer for workers.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in AI Agents
While AI agents are revolutionizing industries and improving efficiency, their rapid advancement also raises critical ethical, legal, and societal challenges. From concerns about data privacy and bias to accountability and job displacement, AI’s increasing autonomy demands careful regulation and ethical considerations.
As AI continues to shape the future, we must address these challenges to ensure that autonomous systems operate fairly, transparently, and responsibly.
1. Data Privacy and Security: Protecting Sensitive Information
AI agents rely on vast amounts of data to function effectively, but how they collect, store, and use that data raises major privacy and security concerns. As AI becomes deeply integrated into healthcare, finance, and customer service, sensitive personal information is at risk of misuse or breaches.
Key Privacy & Security Risks:
- Unauthorized Data Access – AI systems store massive amounts of personal data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks.
- Data Misuse – Companies may use AI-collected data without user consent, leading to ethical concerns.
- AI-Powered Surveillance – Governments and corporations use AI for mass surveillance, raising privacy concerns.
Real-World Concerns:
✅ Facial Recognition Controversy – AI-driven facial recognition has been criticized for privacy violations and surveillance misuse.
✅ Healthcare Data Risks – AI-driven patient records, if hacked, can expose private medical histories.
✅ Social Media Data Exploitation – AI algorithms track user behavior to target ads, often without clear consent.
Potential Solutions:
- Stronger AI Regulations – Governments should enforce privacy laws like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation).
- Data Encryption & Anonymization – AI agents should process data securely without exposing personal information.
- User Transparency – Companies must clearly inform users about how their data is used.
By prioritizing privacy-first AI development, we can protect sensitive data while still benefiting from AI advancements.
2. Bias and Fairness: Preventing Discrimination in AI Decisions
AI agents are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If AI models learn from biased datasets, they can reinforce discrimination and unfair outcomes, particularly in hiring, lending, law enforcement, and healthcare.
How Bias Appears in AI:
- Biased Training Data – If AI learns from biased historical data, it will replicate past discrimination.
- Unequal Algorithmic Outcomes – AI may favor certain groups over others due to unbalanced datasets.
- Lack of Diversity in AI Development – A homogeneous AI research team may unconsciously introduce biases.
Real-World Examples of AI Bias:
✅ AI in Hiring Discrimination – Amazon’s hiring AI showed bias against female candidates because it was trained on male-dominated hiring data.
✅ Racial Bias in Facial Recognition – AI facial recognition systems have higher error rates for people of color, leading to wrongful arrests.
✅ Loan & Credit Score Bias – AI-driven credit approval systems have been found to favor certain demographics, disadvantaging minority groups.
How to Fix AI Bias:
- Diverse & Representative Training Data – AI models should be trained on inclusive datasets to ensure fairness.
- Regular AI Audits – Organizations must conduct bias audits to detect and correct unfair outcomes.
- Transparent AI Decision-Making – AI developers should make AI decision processes explainable to detect biases.
By ensuring equitable AI training and evaluation, we can prevent discriminatory AI outcomes and create fairer autonomous systems.
3. Accountability: Who is Responsible for AI’s Decisions?
As AI agents become more autonomous, a critical question arises: Who is responsible when AI makes a mistake?Unlike traditional tools, AI systems make independent decisions, which complicates accountability in cases of errors, biases, or unintended consequences.
AI Accountability Challenges:
- Legal Responsibility Gaps – If an AI-powered self-driving car crashes, is the blame on the manufacturer, programmer, or owner?
- Lack of Explainability – Many AI models, especially deep learning, function as black boxes, making it difficult to understand their reasoning.
- Autonomous Decision-Making – If an AI medical system misdiagnoses a patient, who should be held responsible?
Real-World Accountability Dilemmas:
✅ Tesla Autopilot Accidents – AI-powered self-driving cars have been involved in fatal crashes, raising legal and ethical concerns.
✅ AI in Criminal Sentencing – Some courts use AI for risk assessment, but inaccurate predictions can lead to unfair prison sentences.
✅ Deepfake Misinformation – AI-generated deepfakes are spreading false information, yet it’s unclear who is accountable.
Proposed Solutions for AI Accountability:
- “Human-in-the-Loop” Systems – AI should assist, not replace, human decision-making in critical applicationslike healthcare and law.
- AI Explainability Standards – Governments should require AI systems to provide clear, interpretable reasonsfor their decisions.
- Legal Frameworks for AI – Lawmakers must define who is responsible when AI systems cause harm.
To build trust in AI, it’s essential to establish clear legal and ethical accountability for autonomous systems.
4. Job Displacement: How AI is Changing the Workforce
One of the biggest concerns surrounding AI is its impact on employment. As AI agents automate customer service, logistics, finance, and even creative work, millions of jobs may become obsolete. However, AI also creates new jobs, requiring workers to reskill and adapt.
Industries Most Affected by AI Automation:
- Manufacturing & Warehousing – AI-powered robots are replacing assembly line workers.
- Customer Service – AI chatbots and virtual assistants are reducing demand for human agents.
- Retail & Cashiering – AI-driven checkout systems like Amazon Go eliminate the need for cashiers.
Real-World Job Disruptions & Adaptations:
✅ Self-Checkout vs. Retail Workers – AI-powered checkout systems are reducing cashier jobs, but also creating tech maintenance roles.
✅ AI in Journalism – AI-generated news reports are replacing some human writers, but new roles in AI content editing are emerging.
✅ Automation in Trucking – Self-driving trucks threaten long-haul trucking jobs, yet demand for AI fleet managers is rising.
How to Address AI Job Displacement:
- Reskilling & Upskilling Programs – Governments and companies should invest in AI and tech training for workers.
- Human-AI Collaboration – Instead of full automation, AI should enhance human jobs (e.g., AI-assisted doctors and teachers).
- Universal Basic Income (UBI) Debate – Some propose UBI as a solution for displaced workers in an AI-driven world.
By focusing on reskilling and job adaptation, society can embrace AI advancements while minimizing worker displacement.
Implications for the Future
How AI Agents Will Shape Society
AI agents are no longer just tools—they are partners in decision-making, automation, and personalization. As these autonomous systems become more advanced, their influence will reshape business, governance, and daily life in profound ways.
The future of AI agents promises hyper-personalized experiences, enhanced human-AI collaboration, global accessibility, and evolving regulations. But as AI’s role grows, we must carefully balance innovation with ethical considerations to ensure it benefits society as a whole.
Let’s explore the most significant future implications of AI agents.
1. Hyper-Personalization: AI Tailoring Experiences to Individuals
One of the most exciting developments in AI is its ability to create highly personalized experiences. Whether in entertainment, healthcare, education, or e-commerce, AI agents are learning individual preferences and behaviors to deliver uniquely tailored services.
How AI is Enabling Hyper-Personalization:
- AI-Powered Recommendations – AI predicts what users will like (e.g., Netflix, Spotify, and e-commerce platforms).
- Personalized Healthcare – AI suggests treatments based on genetic data, medical history, and lifestyle.
- Adaptive Learning – AI tutors customize lesson plans based on a student’s learning style.
Real-World Examples:
✅ Netflix & Spotify’s AI recommendations – AI curates customized playlists and movie suggestions based on user behavior.
✅ AI in Retail (Amazon, Shopify) – AI predicts what products a user will buy next, offering discounts in real-time.
✅ AI in Healthcare (Google DeepMind) – AI tailors treatment plans and medication recommendations for individual patients.
The Future of Hyper-Personalization:
- AI will create ultra-personalized virtual assistants that manage everything from schedules to mental health support.
- AI-driven customized advertisements and marketing will become so precise that companies will predict consumer needs before they arise.
- Ethical challenge – AI must balance personalization with privacy to prevent intrusive surveillance.
Hyper-personalization will make services more efficient and intuitive, but it also raises questions about data privacy and ethical AI marketing.
2. Enhanced Collaboration: AI & Humans Working as a Team
Rather than replacing human workers, AI agents will increasingly act as collaborators, enhancing decision-making and automating repetitive tasks while allowing humans to focus on creativity and strategy.
How AI is Enhancing Human Collaboration:
- AI-Augmented Decision-Making – AI provides data-driven insights, helping professionals in healthcare, finance, and engineering.
- AI as a Co-Creator – AI-generated art, music, and content are revolutionizing creative industries.
- AI in the Workplace – AI-powered assistants handle scheduling, email filtering, and workflow automation.
Real-World Examples:
✅ AI-assisted surgeries – AI helps surgeons perform precision-based procedures with robotic assistance.
✅ AI in journalism – News agencies like Reuters use AI to generate real-time news reports, while humans handle in-depth analysis.
✅ AI in customer service – AI chatbots assist human agents, handling simple tasks while forwarding complex issues to people.
The Future of Human-AI Collaboration:
- AI will work alongside engineers, doctors, teachers, and creatives, not replacing them but amplifying their capabilities.
- AI will become a true “team member” in workplaces, making real-time suggestions, handling administrative work, and enhancing productivity.
- Ethical challenge – We must ensure AI remains a tool for augmentation, not full automation, to prevent over-reliance and job loss.
The future will see AI and humans working as partners, blending automation with human intuition to drive innovation.
3. Global Accessibility: AI Bridging the Digital Divide
AI has the potential to democratize access to information, education, healthcare, and financial services—especially in underserved regions where resources are limited. Autonomous AI tools can help bridge the global digital divide and increase economic opportunities for millions.
How AI is Enhancing Global Accessibility:
- AI-Powered Education – AI tutors offer personalized learning in multiple languages, making education more inclusive.
- Telemedicine & AI Healthcare – AI diagnoses diseases remotely, helping areas with a shortage of doctors.
- Financial Inclusion – AI-powered digital banking helps people in unbanked regions access financial services.
Real-World Examples:
✅ Duolingo AI language tutors – AI personalizes lessons for non-native speakers, making education more accessible.
✅ AI in Rural Healthcare – AI-driven telehealth platforms provide medical advice to people in remote areas.
✅ AI Microfinance Solutions – AI-powered apps like Tala provide loans to individuals with no credit history, helping small businesses grow.
The Future of AI in Accessibility:
- AI-driven real-time translation will break language barriers in business, diplomacy, and education.
- AI-powered smart assistants will help people with disabilities navigate daily life more easily.
- Ethical challenge – AI must be made affordable and accessible to prevent widening the digital divide instead of closing it.
AI has the potential to empower billions by providing services that were previously inaccessible, leveling the global playing field.
4. Regulatory Evolution: The Need for Adaptive AI Policies
As AI agents become more powerful and autonomous, governments will need to adapt their regulations to keep pace with rapid advancements. The challenge is to balance innovation with accountability, fairness, and security.
Key Areas Requiring Regulation:
- AI Transparency & Explainability – Users should know how AI makes decisions.
- Bias & Fairness Laws – AI models should undergo audits to ensure ethical and unbiased decision-making.
- AI in Employment & Automation – Policies should address job displacement and reskilling initiatives.
- AI & National Security – Regulations must control the use of AI in surveillance, warfare, and deepfake misinformation.
Real-World Regulatory Challenges:
✅ EU’s AI Act – The European Union is leading the way with strict AI laws governing privacy, bias, and high-risk AI applications.
✅ U.S. AI Oversight Debates – The U.S. is discussing AI regulations in sectors like healthcare, finance, and policing.
✅ China’s AI Surveillance Policies – China’s AI regulations are focused on national security and censorship, raising human rights concerns.
The Future of AI Regulation:
- Governments will create global AI regulatory bodies, similar to how financial markets and nuclear technologyare governed.
- Ethical AI development will be a legal requirement, ensuring AI systems follow human rights principles.
- Ethical challenge – AI regulations must prevent misuse without stifling innovation, striking a delicate balance.
The world must move quickly to ensure that AI is developed, deployed, and regulated responsibly, preventing potential misuse or harmful consequences.
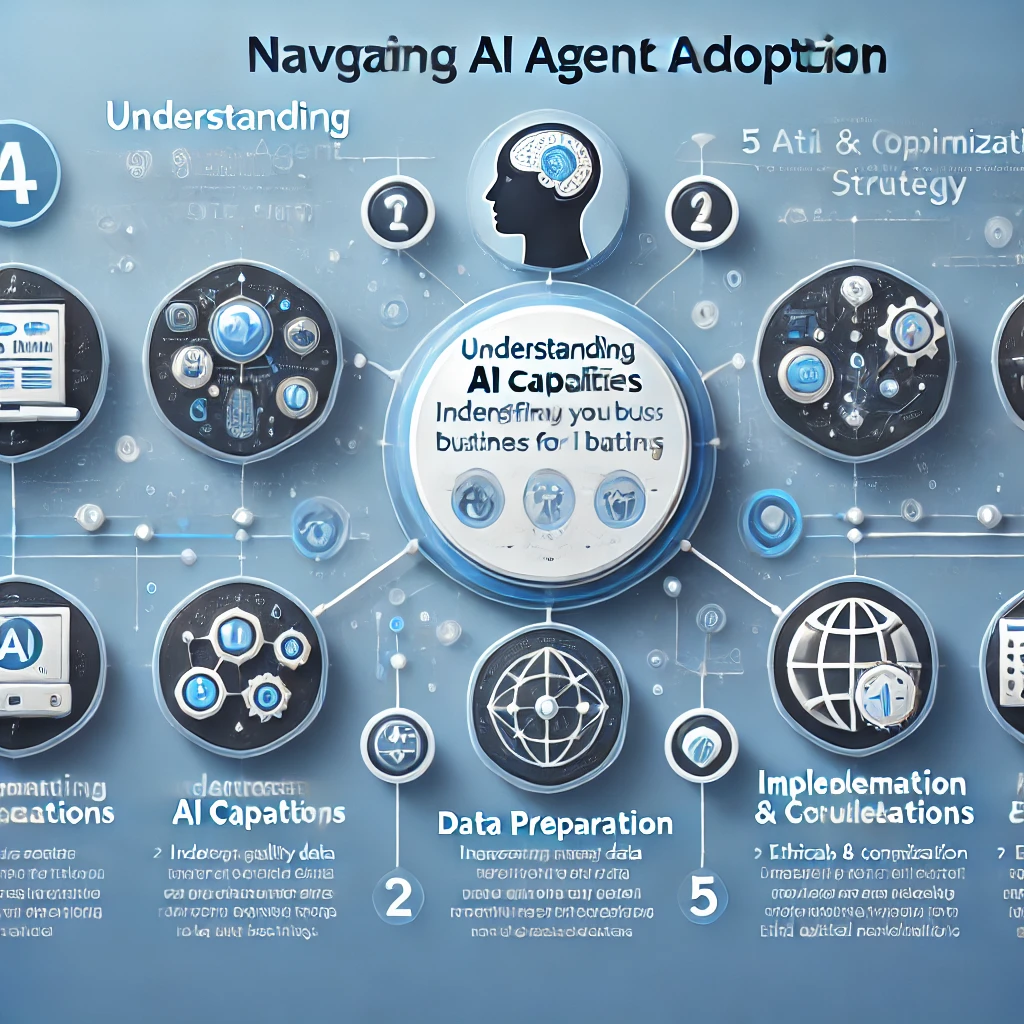
Navigating AI Agent Adoption
A Strategic Guide
AI agents are rapidly transforming industries, enhancing efficiency, and redefining business operations. However, adopting AI is not without challenges—businesses must navigate technological hurdles, ethical concerns, and integration complexities to fully harness AI’s potential.
This guide explores how organizations can overcome key AI adoption challenges and outlines practical first steps for integrating AI agents into business operations.
1. Overcoming Challenges: Strategies to Address Technological & Ethical Hurdles
While AI adoption offers immense benefits, businesses must address several key challenges, including technical limitations, ethical risks, workforce adaptation, and regulatory compliance.
Key Challenges & Solutions:
A. Data Quality & Infrastructure Gaps
AI agents thrive on high-quality, structured data, but many businesses struggle with incomplete, biased, or siloed data.
✔ Solution:
✅ Implement data governance frameworks to ensure clean, structured, and unbiased data.
✅ Adopt cloud-based AI solutions for scalable and secure data storage.
✅ Leverage synthetic data generation to fill data gaps and train AI models effectively.
B. Ethical & Bias Concerns
AI models can inadvertently reinforce biases, leading to unfair outcomes in hiring, lending, healthcare, and law enforcement.
✔ Solution:
✅ Conduct regular AI bias audits to detect and mitigate biased decision-making.
✅ Use diverse datasets to train AI models and ensure fairness.
✅ Implement transparent AI decision-making to explain AI-driven outcomes.
C. Workforce Resistance & Job Displacement
Employees may fear that AI will replace jobs, leading to resistance to AI adoption.
✔ Solution:
✅ Position AI as a collaborative tool, not a replacement, emphasizing augmentation over automation.
✅ Provide AI upskilling programs to train employees in AI-driven workflows.
✅ Foster a culture of AI trust and transparency, involving employees in AI deployment strategies.
D. Regulatory & Compliance Issues
Governments are increasing AI regulations, requiring businesses to comply with data privacy, security, and fairness laws.
✔ Solution:
✅ Stay updated on AI laws like the EU AI Act, GDPR, and U.S. AI policies.
✅ Implement explainable AI (XAI) practices to comply with transparency requirements.
✅ Establish AI ethics boards to oversee responsible AI use in business operations.
By proactively addressing these challenges, businesses can adopt AI responsibly and gain a competitive edge.
2. First Steps to AI Adoption: How Businesses Can Integrate AI Agents into Operations
Successfully integrating AI requires a strategic, phased approach. Businesses should start small, align AI adoption with key business goals, and gradually expand AI capabilities.
Step 1: Identify AI Use Cases Aligned with Business Goals
Instead of adopting AI for the sake of innovation, companies must define clear AI objectives that solve specific business challenges.
✔ Examples of AI Use Cases by Industry:
✅ Retail & E-commerce – AI-driven personalized recommendations, inventory optimization.
✅ Healthcare – AI-powered diagnostics, predictive analytics for patient care.
✅ Finance – AI fraud detection, automated customer service chatbots.
✅ Manufacturing – AI-powered predictive maintenance, robotic process automation.
✔ Actionable Tip:
🔹 Conduct an internal AI-readiness assessment to identify the most impactful AI applications for your business.
Step 2: Start with Pilot Projects & Measure ROI
A common mistake is rushing full-scale AI deployment without first testing small-scale AI initiatives.
✔ How to Run a Successful AI Pilot:
✅ Choose one department (e.g., customer service, supply chain, or HR) for AI testing.
✅ Implement AI in low-risk, high-impact areas, such as automating repetitive tasks.
✅ Define KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) like cost reduction, efficiency improvement, and customer satisfaction.
✅ Collect feedback from employees and stakeholders to refine AI implementation.
✔ Actionable Tip:
🔹 Use AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) solutions (like Google AI, AWS AI, or Microsoft Azure AI) for low-cost AI experimentation.
Step 3: Build an AI-Ready Workforce
AI success depends on human-AI collaboration. Organizations must train employees to work alongside AI agents and develop AI literacy across all departments.
✔ AI Workforce Development Strategies:
✅ Offer AI training programs for employees to learn AI-related skills.
✅ Encourage a culture of AI innovation, where employees contribute AI-driven ideas.
✅ Hire AI specialists & data scientists to lead AI initiatives.
✔ Actionable Tip:
🔹 Partner with online AI learning platforms (Coursera, Udacity, LinkedIn Learning) to upskill employees.
Step 4: Ensure AI is Ethical, Transparent & Secure
AI adoption must align with ethical principles, ensuring that AI operates transparently, fairly, and securely.
✔ How to Build Ethical AI Practices:
✅ Implement AI governance frameworks to monitor AI risks and biases.
✅ Ensure AI models are explainable (XAI) and accountable for their decisions.
✅ Follow privacy laws like GDPR and implement strong cybersecurity measures.
✔ Actionable Tip:
🔹 Create an AI Ethics Committee to oversee AI decision-making and compliance.
Step 5: Scale AI Adoption Gradually
Once AI proves successful in pilot projects, organizations can expand AI adoption to optimize multiple business functions.
✔ AI Scaling Strategies:
✅ Integrate AI with existing enterprise systems (CRM, ERP, cloud services, IoT).
✅ Automate more complex workflows beyond initial pilot use cases.
✅ Monitor AI performance with continuous testing & feedback loops.
✔ Actionable Tip:
🔹 Use AI-driven analytics to measure AI’s impact on business performance and optimize strategies.
Embracing the Future of Autonomous AI Agents
Autonomous AI agents are no longer a concept of the future—they are here, reshaping industries, redefining decision-making, and transforming the way we interact with technology. From self-driving cars and AI-driven healthcare diagnostics to intelligent virtual assistants and automated financial advisors, AI agents are rapidly becoming integral to our daily lives.
But with great technological power comes great responsibility. As AI continues to evolve, businesses, governments, and individuals must proactively prepare for the opportunities and challenges it brings.
This article explores the transformative potential of autonomous AI and how different sectors of society can strategically embrace this revolution.
1. The Transformative Potential of Autonomous AI Agents
AI agents are evolving beyond simple automation into self-learning, decision-making entities that can operate with minimal human intervention. Their impact will be felt across multiple domains, enhancing efficiency, decision-making, and personalization at an unprecedented scale.
Key Transformative Impacts of AI Agents:
A. Reshaping Industries with Intelligent Automation
AI agents are revolutionizing traditional industries, automating repetitive tasks, and enhancing decision-making in ways that were once impossible.
✔ Real-World Examples:
✅ Healthcare – AI diagnoses diseases, personalizes treatment plans, and assists in robotic surgeries.
✅ Finance – AI-powered trading bots optimize investments, while AI fraud detection prevents cyber threats.
✅ Retail & E-commerce – AI predicts consumer preferences, automates inventory management, and enhances customer experiences.
✅ Manufacturing – AI-driven robots optimize production lines, improving efficiency and reducing human labor risks.
B. Enabling Personalized & Adaptive Experiences
AI agents are making hyper-personalization the new standard, offering customized solutions tailored to individual needs.
✔ How AI is Driving Personalization:
✅ Smart Assistants – AI-powered voice assistants (Alexa, Google Assistant) learn from user interactions to provide tailored recommendations.
✅ AI in Education – Personalized AI tutors adjust learning content based on student progress.
✅ AI in Healthcare – Predictive AI identifies disease risks before symptoms appear, offering personalized health plans.
C. Enhancing Decision-Making with AI-Augmented Intelligence
AI agents process vast amounts of data faster than humans, providing real-time insights that improve decision-making.
✔ How AI is Supporting Human Decisions:
✅ Business Strategy – AI-driven analytics identify market trends, guiding executives in data-backed decision-making.
✅ Government Policy – AI assists policymakers in analyzing economic patterns, climate change data, and crisis management.
✅ Legal Industry – AI-powered legal assistants help lawyers analyze case law and draft contracts more efficiently.
D. Strengthening Cybersecurity & Risk Management
AI agents are essential in combating cyber threats, detecting fraud, and ensuring real-time security monitoring.
✔ How AI Improves Security:
✅ AI in Fraud Detection – AI algorithms identify suspicious transactions and prevent financial fraud.
✅ AI-Powered Cybersecurity – AI detects and responds to cyberattacks before they cause significant damage.
✅ Autonomous AI in National Security – Governments use AI for threat detection, border security, and military intelligence.
Autonomous AI is reshaping society, but its success depends on how well we prepare for its widespread integration.
2. Preparing for the AI-Driven Future
For AI to be adopted effectively, businesses, governments, and individuals must take proactive steps to adapt, regulate, and integrate AI responsibly.
A. How Businesses Can Prepare for AI Agents
✔ AI Strategy & Workforce Transformation:
✅ Develop a clear AI adoption strategy aligned with business goals.
✅ Train employees in AI literacy, focusing on collaboration between humans and AI.
✅ Invest in ethical AI governance to ensure fair, transparent, and unbiased AI decision-making.
✔ AI-Driven Innovation & Digital Transformation:
✅ Integrate AI-powered chatbots, automation tools, and predictive analytics to streamline operations.
✅ Use AI for customer personalization, improving user experiences and engagement.
✅ Foster an AI innovation culture, encouraging employees to explore new AI-driven solutions.
✔ AI & Cybersecurity Considerations:
✅ Implement AI-powered cybersecurity tools to protect sensitive business data.
✅ Regularly audit AI systems to eliminate biases, enhance security, and improve efficiency.
B. How Governments Can Prepare for AI Agents
Governments play a critical role in shaping AI policies, ensuring ethical use, and addressing AI-driven societal changes.
✔ Developing AI Regulations & Ethical Guidelines:
✅ Establish laws governing AI transparency, bias mitigation, and accountability.
✅ Promote AI research in public safety, environmental sustainability, and urban development.
✅ Encourage AI innovation while ensuring AI safety and human oversight.
✔ Preparing for AI’s Economic & Workforce Impact:
✅ Invest in AI upskilling programs to help workers transition to AI-driven jobs.
✅ Support businesses in responsible AI adoption, preventing mass job displacement.
✅ Address AI-driven economic shifts, ensuring fair AI taxation and wealth distribution.
✔ AI in National Security & Public Services:
✅ Use AI in smart city planning, traffic management, and disaster response.
✅ Strengthen AI-powered law enforcement tools while ensuring privacy rights.
✅ Implement AI in public healthcare systems for early disease detection and outbreak prevention.
Governments must balance AI-driven innovation with ethical considerations, ensuring AI serves humanity’s best interests.
C. How Individuals Can Prepare for AI Agents
AI is becoming deeply integrated into daily life—individuals must develop AI literacy, adapt to AI-driven work environments, and ensure responsible AI usage.
✔ AI Literacy & Education:
✅ Learn about AI basics, its benefits, and its risks.
✅ Take AI-related courses on data literacy, automation, and AI ethics.
✅ Stay informed about AI developments to adapt to future job market shifts.
✔ AI in the Workplace & Career Planning:
✅ Embrace AI-powered tools to enhance productivity and decision-making.
✅ Develop skills in data analysis, AI ethics, and human-AI collaboration.
✅ Consider careers in AI-driven industries, such as robotics, cybersecurity, and AI policy.
✔ Ensuring AI is Used Ethically & Responsibly:
✅ Protect personal data by understanding AI-driven privacy policies.
✅ Advocate for transparent, fair, and unbiased AI practices in businesses and government.
✅ Support AI initiatives that promote human rights, environmental sustainability, and societal well-being.
By actively learning, adapting, and advocating for ethical AI, individuals can thrive in the AI era rather than fear it.
Conclusion
The Future of AI Agents – Innovation with Responsibility
Autonomous AI agents are revolutionizing industries, reshaping automation, and paving the way for a more intelligent, efficient, and adaptive future. From enhancing decision-making and streamlining workflows to personalizing user experiences and optimizing complex processes, AI agents are no longer just supporting tools—they are active participants in shaping the digital economy.
However, with this transformation comes great responsibility. The rapid rise of AI agents demands ethical foresight, regulatory frameworks, and proactive governance to ensure that AI serves humanity fairly, safely, and transparently. Without clear guidelines, we risk biases in AI decision-making, job displacement, data privacy threats, and accountability challenges.
To fully harness AI’s potential, businesses, governments, and individuals must collaborate in building a responsible AI ecosystem. Organizations must prioritize AI ethics and transparency, governments must establish adaptive regulations, and individuals must develop AI literacy to navigate this new era confidently.
A Call to Action
The rise of AI agents presents a once-in-a-generation opportunity to redefine how we work, live, and innovate. Whether AI becomes a force for good or a source of disruption depends on the choices we make today. By embracing ethical AI adoption, fostering responsible innovation, and ensuring human oversight, we can shape a future where AI empowers, rather than replaces, humanity.
The future of automation is here—are we ready to guide it responsibly?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on The Rise of Autonomous AI Agents: Shaping the Future of Automation
1. What are autonomous AI agents?
Autonomous AI agents are self-operating artificial intelligence systems that can make decisions, adapt to changes, and perform tasks with minimal human intervention. They leverage technologies like machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and reinforcement learning to analyze data, predict outcomes, and execute actions efficiently.
2. How do autonomous AI agents differ from traditional AI systems?
Traditional AI systems typically follow predefined rules and require human input for decision-making. In contrast, autonomous AI agents learn from data, adapt to new scenarios, and operate independently, making them more flexible and capable of handling complex, dynamic environments.
3. What industries are benefiting from autonomous AI agents?
Autonomous AI agents are transforming multiple industries, including:
✅ Healthcare – AI-powered diagnostics, robotic surgery assistants, and personalized treatment recommendations.
✅ Finance – Automated trading bots, fraud detection, and AI-driven risk analysis.
✅ Retail & E-commerce – AI chatbots for customer support, personalized shopping recommendations, and supply chain optimization.
✅ Manufacturing – AI-driven robotics, predictive maintenance, and automated production lines.
✅ Transportation – Self-driving vehicles, AI-powered traffic management, and logistics automation.
4. How do autonomous AI agents make decisions?
AI agents make decisions based on data analysis, pattern recognition, and predictive modeling. They use techniques like:
- Machine learning (ML) – Learning from past data to improve future performance.
- Natural language processing (NLP) – Understanding and responding to human language.
- Reinforcement learning – Learning through trial and error to optimize decision-making.
5. What are the key benefits of using autonomous AI agents?
✔ Increased Efficiency – AI agents automate repetitive tasks, reducing workload and operational costs.
✔ Improved Accuracy – AI minimizes human errors in decision-making and data processing.
✔ 24/7 Availability – Unlike humans, AI agents can operate continuously without fatigue.
✔ Scalability – AI can handle vast amounts of data and scale operations effortlessly.
✔ Personalization – AI-driven recommendations enhance user experiences in sectors like e-commerce and healthcare.
6. What challenges do businesses face when adopting AI agents?
Despite their benefits, AI adoption comes with challenges such as:
⚠ Data Privacy & Security Risks – Ensuring sensitive data is protected from cyber threats.
⚠ AI Bias & Fairness – Preventing AI from making biased or discriminatory decisions.
⚠ Job Displacement Concerns – Addressing fears about AI replacing human jobs.
⚠ Regulatory & Compliance Issues – Adapting to evolving AI laws and governance frameworks.
⚠ Integration Complexity – Merging AI with existing business systems and workflows.
7. Will AI agents replace human jobs?
While AI will automate many tasks, it will also create new job opportunities in areas like AI development, ethics oversight, and human-AI collaboration. Rather than replacing jobs entirely, AI will augment human capabilities, allowing people to focus on more strategic and creative tasks. The key is workforce upskilling and reskilling to adapt to AI-driven job markets.
8. How can businesses prepare for AI agent adoption?
To successfully integrate AI, businesses should:
✅ Start with small-scale AI pilot projects before full implementation.
✅ Invest in AI training programs for employees.
✅ Ensure AI ethics and transparency in decision-making.
✅ Leverage AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS) platforms for scalable adoption.
✅ Develop a long-term AI strategy aligned with business goals.
9. What role do governments play in AI regulation?
Governments must create policies that ensure ethical AI use, data privacy, and fairness. This includes:
✔ Establishing AI transparency and accountability laws.
✔ Regulating AI-driven decision-making in critical sectors (healthcare, finance, law enforcement, etc.).
✔ Ensuring AI does not reinforce societal biases.
✔ Promoting AI research and innovation while safeguarding public interests.
10. What ethical concerns arise with AI agents?
AI ethics revolves around issues such as:
⚠ Bias & Fairness – AI systems may develop biases if trained on unbalanced datasets.
⚠ Accountability – Who is responsible if an AI makes an incorrect or harmful decision?
⚠ Data Privacy – Ensuring AI does not misuse personal data.
⚠ Autonomy vs. Human Oversight – Finding the right balance between AI decision-making and human control.
11. Can AI agents be hacked or manipulated?
Yes, AI agents can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, such as:
- Adversarial attacks – Manipulating AI models with deceptive data inputs.
- Data poisoning – Injecting biased or harmful data to corrupt AI training.
- AI-driven phishing – Using AI to automate and refine cyberattacks.
To counter these risks, businesses must invest in robust AI security frameworks, including regular AI audits, encryption, and anomaly detection systems.
12. What is the future of autonomous AI agents?
AI agents will continue evolving, leading to:
✔ Hyper-personalization – AI tailoring services to individual needs with unprecedented accuracy.
✔ Human-AI collaboration – AI becoming a co-worker rather than a replacement.
✔ Decentralized AI systems – Reducing reliance on centralized AI control for greater transparency.
✔ AI-augmented governance – Governments using AI for policy-making, urban planning, and crisis management.
13. How can individuals prepare for an AI-driven future?
To thrive in an AI-powered world, individuals should:
✅ Learn AI-related skills, such as data literacy, machine learning, and AI ethics.
✅ Stay updated on AI trends and industry shifts.
✅ Develop critical thinking skills to assess AI-driven recommendations and decisions.
✅ Advocate for responsible AI development and usage in society.
14. How do AI agents learn and improve over time?
AI agents learn and improve through machine learning (ML) techniques, particularly:
✔ Supervised Learning – Learning from labeled datasets to make predictions.
✔ Unsupervised Learning – Identifying patterns in unlabeled data.
✔ Reinforcement Learning (RL) – Learning through trial and error, where the agent receives rewards or penalties for its actions.
✔ Deep Learning – Using neural networks to process complex patterns and improve decision-making.
By continuously analyzing new data, AI agents refine their algorithms, improve accuracy, and adapt to changing environments.
15. What is the difference between AI agents and AI-powered automation?
- AI-powered automation follows predefined rules and scripts to execute repetitive tasks (e.g., chatbots with scripted responses).
- AI agents, on the other hand, are autonomous, adaptive, and decision-making entities capable of learning from data and responding dynamically to new situations.
16. Can AI agents collaborate with each other?
Yes, AI agents can work together in multi-agent systems (MAS), where multiple AI entities:
✔ Communicate and share data to optimize decision-making.
✔ Coordinate actions to solve complex problems (e.g., AI-powered supply chains).
✔ Compete and negotiate in strategic environments (e.g., AI agents in financial trading).
Such collaborative AI networks enable higher efficiency and more sophisticated automation.
17. How do AI agents handle unpredictable or unfamiliar situations?
AI agents use reinforcement learning and probabilistic reasoning to make the best possible decisions in uncertain environments. They:
✔ Analyze similar past experiences to make informed guesses.
✔ Use real-time data processing to adjust responses.
✔ Seek human intervention when a situation exceeds their learning boundaries.
This adaptability makes AI agents particularly useful in fields like disaster response, cybersecurity, and autonomous vehicles.
18. Are AI agents capable of creativity and independent thought?
While AI can generate creative content (e.g., AI-generated art, music, or writing), it lacks true independent thought and emotions. AI creativity is based on pattern recognition and data synthesis rather than genuine human intuition or consciousness.
19. What role do AI agents play in cybersecurity?
AI agents are increasingly being used to:
✔ Detect and prevent cyberattacks by analyzing threats in real time.
✔ Identify suspicious activities in financial transactions (fraud detection).
✔ Automate security updates and vulnerability scans.
✔ Respond to security breaches faster than human analysts.
However, AI can also be exploited for cyberattacks, making AI security a critical area of focus.
20. How do AI agents affect human decision-making?
AI agents assist humans by providing data-driven insights that enhance decision-making in various fields:
✔ Medicine – AI helps doctors diagnose diseases with greater accuracy.
✔ Finance – AI predicts market trends and helps investors make smarter choices.
✔ Retail – AI personalizes shopping recommendations based on customer preferences.
However, over-reliance on AI without human oversight can lead to biased or flawed decisions.
21. Can AI agents feel emotions or understand human emotions?
AI agents can detect and analyze emotions through technologies like sentiment analysis and facial recognition, but they do not “feel” emotions like humans. Their responses are based on data interpretation rather than genuine emotional experience.
22. How do AI agents impact environmental sustainability?
AI plays a significant role in promoting sustainability by:
✔ Optimizing energy consumption in smart grids and industrial processes.
✔ Reducing waste in supply chains and logistics.
✔ Enhancing climate modeling to predict and mitigate environmental risks.
✔ Automating precision agriculture to reduce water and fertilizer usage.
23. How do businesses measure the success of AI agent adoption?
Success is measured through:
✔ Efficiency Gains – Reduction in operational costs and time.
✔ Accuracy Improvements – Lower error rates in decision-making.
✔ Customer Satisfaction – Enhanced user experience and engagement.
✔ Revenue Growth – Increased productivity and sales from AI-driven insights.
✔ Ethical AI Compliance – Transparency, fairness, and security in AI decision-making.
24. Are there risks of AI agents surpassing human intelligence?
The idea of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)—where AI surpasses human intelligence across all domains—remains theoretical. Current AI agents are narrow AI systems designed for specific tasks and lack true human-like reasoning, emotions, and self-awareness.
25. How will AI agents shape the future of automation?
AI agents will:
✔ Make automation more adaptive, intelligent, and self-sufficient.
✔ Enable hyper-personalization in business and customer service.
✔ Improve efficiency and accuracy across industries.
✔ Increase human-AI collaboration, rather than full automation replacing human workers.